The Talent War Is a Data War
In today’s global labor market, companies are hemorrhaging talent. Traditional retention strategies based on perks, corporate culture, or managerial gut-feel are proving insufficient in the face of rising turnover. The battlefield has shifted: talent retention is now a data‑driven contest. Modern Human Resource Technology (HR technology) is the new strategic weapon, turning human‑resource management into a science of prediction and precision. This article argues that embracing AI‑driven HR analytics, robust People Analytics and embedded Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) metrics isn’t optional: it’s the decisive edge for companies serious about retention.
The Evolution of HR Technology: From Gut Feeling to Data Science
Why Legacy HR Methods Are Failing Employee Retention
Legacy HR relied on subjective judgment, anecdotal feedback and generalized policies. Managers made promotion or retention calls based on personal impressions. These methods fail to catch silent disengagement; they miss systemic issues like micro‑inequities, culture drift, or subtle dissatisfaction. As a result, many employees quietly disengage, often leaving without warning. Without data, companies are blind to early warning signs.
How Modern HR Technology Drives Precision in Talent Management
HR technology collects real-time and historical workforce data as performance, engagement, compensation, mobility, feedback and more. This enables companies to proactively craft personalized retention strategies, target high‑risk segments, and allocate resources where they matter. Data‑driven HR transforms HR from being reactive to proactive, reducing attrition and aligning workforce planning with business strategy.
People Analytics: The Predictive Edge in Retention
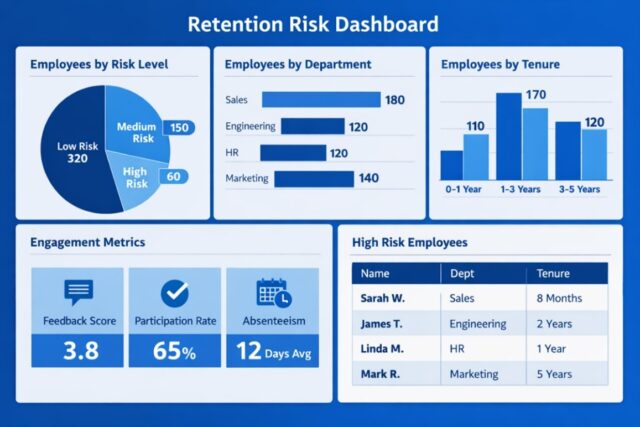
Using People Analytics to Identify Flight Risks Early
People Analytics aggregates and analyzes workforce data to deliver predictive insights: who is likely to leave, which departments show disengagement, when to intervene. It reveals patterns invisible to the naked eye declines in engagement, stalling career paths, demographic or role‑based attrition. Organizations that deploy People Analytics gain foresight and can act before turnover spikes. Recent studies confirm People Analytics improves retention by helping organizations “understand employee behavior, satisfaction drivers, and engagement levels.” (hrmob.org)
From Insight to Action: Embedding Analytics into HR Workflows
Predictive scores and risk heatmaps only matter if integrated into HR workflows. Once high‑risk individuals or teams are flagged, HR can trigger early interventions targeted at coaching, career conversations, targeted DEI efforts, or workload adjustments. Embedding People Analytics seamlessly into talent‑management workflows ensures data drives decisions, not bias or guesswork.
Employee Retention Risk Scoring
HR Analytics vs HR Intuition: The Cold Truth
Why “Manager Instincts” Are No Match for Algorithmic Insight
Managerial instincts are shaped by personal biases, memory, and limited visibility. They rarely capture systemic trends across the organization. In contrast, HR analytics analyzes data on a scale such as performance, mobility, tenure, feedback, demographics, exit reasons. It standardizes decision‑making, reduces unconscious bias, and surfaces structural issues like pay gaps, inequitable promotions, or departments with high attrition.
The Accountability Problem in Non‑Data‑Driven HR
Without metrics, decisions remain opaque and unaccountable. It becomes easy to misattribute turnover to “bad attitudes” or “lack of loyalty,” rather than root causes like unequal career opportunities or cultural alienation. By contrast, HR analytics provides transparent evidence, enabling leaders to trace outcomes to interventions.
metrics comparison:
| Metric Type | Traditional HR KPIs | HR Analytics Metrics |
| Talent turnover | Annual turnover rate | Monthly attrition risk score, voluntary vs involuntary breakdown |
| Performance evaluation | Qualitative reviews | Performance trend by tenure, peer feedback score, productivity data |
| Engagement | Pulse survey every 1–2 years | Real‑time sentiment, feedback frequency, workload indicators |
| DEI (equity) | Headcount by demographic | Promotion rate by demographic, pay equity index, retention by group |

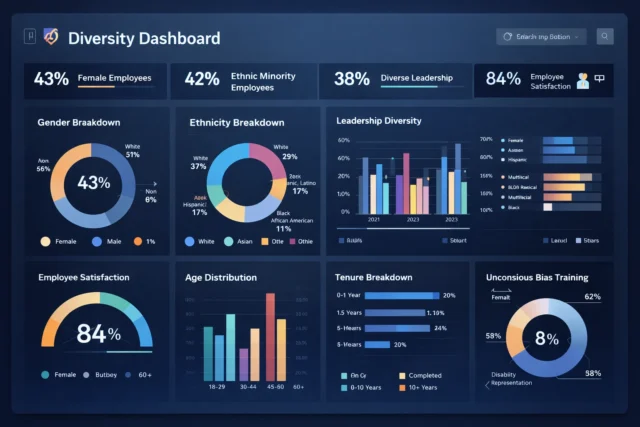
DEI in the Data Age: From Lip Service to Strategic Leverage
Why DEI Initiatives Fail Without HR Technology
DEI efforts often remain aspirational slogans when they lack measurement. Without data, companies can’t know if promotions are equitable, if certain groups churn faster, or if pay gaps persist. HR technology enables quantifiable DEI metrics like promotion equity, pay equity, representation, and attrition by demographic. Without data, DEI remains a checkbox, not a lever for retention.
Real‑Time DEI Metrics as a Retention Accelerator
When DEI metrics feed into People Analytics dashboards, companies can detect early if underrepresented groups are leaving at higher rates. Interventions such as mentorship, equitable promotion policies, targeted retention bonuses, can then be deployed promptly. Real‑time metrics also signal to employees that DEI isn’t rhetorical but operational. That boosts trust, belonging and retention.
Key DEI metrics to track via HR technology:
- Promotion rate by demographic (gender, ethnicity, age)
- Pay equity index across roles and demographics
- Retention rate by demographic
- Representation in leadership and high‑potential pools
- Inclusion sentiment (surveys, feedback, engagement scores)
Surveillance or Support? The Ethics of Retention Tech
Employee Monitoring Tools: Empowerment or Overreach?
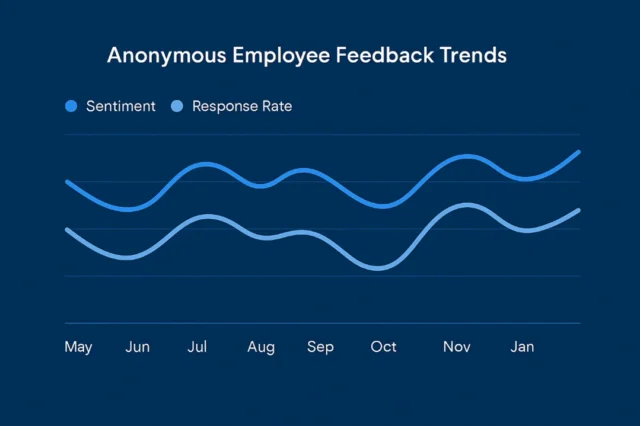
Some companies deploy HR technology as surveillance like tracking keystrokes, attendance, activity logs. While this may yield data, over-monitoring erodes trust and can backfire. Research warns that excessive monitoring may reduce morale, foster paranoia, and lead employees to disengage or leave. (BrianHeger.com)
Transparency as the Missing Link in Tech‑Driven Retention
Ethical deployment of HR analytics requires transparency, clarity about what data is collected, how it’s used, and who sees it. Organizations must communicate proactively, offer opt‑outs or anonymized feedback, and ensure data protects rather than punishes employees. When done right, HR technology becomes support not surveillance.
Why CHROs Need to Think Like Data Scientists
Data Fluency as a Core HR Leadership Competency
HR leaders can no longer rely solely on soft skills; they need data fluency. Understanding metrics, analytics, forecasting and modeling is becoming essential. HR technology makes data literacy a core leadership competency. Only leaders who understand data can ask the right questions and steer retention strategies effectively.
Building Cross‑Functional Alliances with IT and Data Teams
Effective deployment of HR technology requires collaboration between HR, data/data science teams, and IT. HR must partner with analytics specialists to build pipelines, dashboards, privacy safeguards, and measurement frameworks. This cross‑functional alliance ensures HR analytics becomes an organizational capability not just a set of ad‑hoc reports.
skills gap:
| Traditional HR Leader Skills | Data‑Savvy CHRO Skills (with HR technology) |
| Talent management, employee relations, compliance | Data interpretation, predictive modeling, data governance, privacy |
| Generalist HR knowledge | Cross-functional collaboration with IT, analytics, business leaders |
Vendor Lock‑In or Strategic Ecosystem? Choosing the Right HR Technology
Open Systems vs Closed Suites in HR Tech
When selecting HR technology, companies face a fork: closed, all‑in‑one suites vs open, modular systems. Closed suites offer turnkey solutions but risk vendor lock-in and limited flexibility. Open systems (plug-ins, modular dashboards, API‑based tools) offer flexibility, customization, and future‑proofing essential in a rapidly changing HR landscape.
What to Ask Before Investing in Any Retention Platform
Before committing, companies should evaluate:
- Integration capabilities with existing HR and business systems
- Customization vs rigidity (can you build custom analytics?)
- Scalability as employee base grows or business pivots
- Data privacy and governance features
- Transparency and employee consent mechanisms
Key vendor evaluation criteria:
- API support and interoperability
- Custom dashboard and modeling capabilities
- Data ownership and export policies
- Privacy compliance (GDPR or local privacy laws)
- Ease of use for HR staff (non‑technical friendly)
HR Technology Is the Future of Retention
Employee retention is no longer a soft skill; it is a data discipline. Organizations that cling to traditional HR practices risk being blindsided by quiet attrition. In contrast, those that embrace HR technology, embed People Analytics, and operationalize DEI metrics transform HR into a strategic advantage. The ethical concerns about surveillance, privacy, bias are real, but manageable through transparency and governance. The choice is stark: companies that ignore the data war will lose talent; companies that master it will win loyalty and long‑term performance.
The future of talent retention belongs to those who treat employees not as abstract resources, but as data‑defined humans: understood, empowered, and engaged through technology.
References
- How People Analytics Can Help You Change Process, Culture, and Strategy – Harvard Business Review
- The New Possible: How HR Can Help Build the Organization of the Future – McKinsey & Company
- People Analytics: Recalculating the Route – Deloitte Insights
- How Companies Can Improve Employee Engagement Right Now – Harvard Business Review
- The Future of Work: How HR Leaders Are Rewriting the Rules – World Economic Forum
- Real-Time Feedback in HR Tech: Boost or Big Brother?



