The New Frontier of Market Research
In 2030, Market Research stands on the razor’s edge between unparalleled insight and catastrophic misinformation. For decades, businesses have clung to human expertise to interpret customer sentiment and competitive dynamics. Today, AI promises faster, cheaper, and seemingly more accurate outcomes through automated data collection and pattern recognition. Yet, speed without scrutiny breeds blind spots. As companies ask how to decode customer sentiment with machine precision, the central question transcends technology: does automation elevate customer satisfaction understanding or erode it through hidden biases and algorithmic shortcuts? Leaders championing AI tools cite unprecedented scale and predictive power, as discussed in Deloitte’s perspectives on human‑AI collaboration and enterprise transformation.(Deloitte) Yet critics warn that over‑automation risks replacing context with noise, a theme explored in the Harvard Business Review’s analysis of AI tools transforming market research.(Harvard Business Review) The real debate for 2030 will be whether automation enhances strategic clarity or simply accelerates expensive mistakes.
Market Research and the Rise of AI-Powered Data Collection
From Surveys to Sensors: How Data Collection Is Evolving
AI‑driven Market Research redefines data collection by harnessing sensors, digital traces, and real‑time analytics. Traditional surveys are now supplemented or replaced with continuous data streams from IoT devices, social platforms, and digital footprints. This evolution promises deeper behavioral insight at scale, as evidenced in McKinsey’s report on AI adoption and organizational impact.(McKinsey & Company) Yet, automation can miss emotional nuance and context that seasoned researchers capture through qualitative methods. Organizations face a choice: embrace sensor feeds that generate vast datasets or retain human‑centric instruments that capture the “why” behind actions.
Are Algorithms Outpacing Human Insight?
Algorithms can detect patterns invisible to traditional analysis, yet pattern recognition isn’t understanding. AI may flag correlations that mislead strategic decisions if humans fail to vet them. For example, automated sentiment models might misclassify cultural expressions, impacting customer satisfaction metrics. Without skilled interpretation, AI outputs become sophisticated noise.
Critical business research underscores the necessity of human oversight in interpreting machine outputs, as artificial intelligence tools transform market research practices.(Harvard Business Review) Automation accelerates discovery but cannot replace contextual judgment.
Customer Satisfaction in the Age of Machine Interpretation
Sentiment Analysis vs Emotional Nuance
AI‑based sentiment analysis elevates Market Research by rapidly quantifying attitudes across millions of interactions. Yet machines cannot fully grasp irony, cultural subtext, or emotional layers, leading to skewed customer satisfaction scores. When automated tools interpret sarcasm as positive sentiment, businesses may misallocate resources. Companies attempting to automate emotional interpretation without human calibration risk strategic missteps.
AI‑Driven vs Human‑Led Customer Satisfaction Metrics
| Feature | AI‑Driven | Human‑Led |
| Speed | Very Fast | Moderate |
| Contextual Accuracy | Medium | High |
| Cultural Nuance | Low | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Scalability | Very High | Limited |
Are Chatbots Killing the Human Feedback Loop?
Automated chatbots have become the frontline of Market Research feedback loops, answering queries and collecting ratings without human intervention. Chatbots streamline volume management but often miss emotional subtleties and escalate dissatisfaction if mishandled. Firms relying exclusively on chatbot‑derived feedback risk misinterpreting customer frustration as indifference, undermining customer satisfaction strategies.

Research from the IBM Institute for Business Value shows how AI is reshaping customer service, enhancing personalization while highlighting the importance of human oversight to interpret sentiment beyond numerical scores.(IBM)
Predictive Market Research or Prejudiced Forecasting?
Bias in Automated Data Models
AI models are only as unbiased as the data that trains them. Automated Market Research relies on historical datasets that can embed demographic, cultural, or socioeconomic biases. These biases can warp predictive models, causing companies to target the wrong segments or misread emerging trends. Automated does not guarantee fair or accurate.
5 Common Biases in AI‑Driven Market Research
- Sampling bias from unrepresentative datasets
- Labeling bias in sentiment corpora
- Platform bias favoring certain demographics
- Recency bias over‑weighting recent patterns
- Confirmation bias embedded in model objectives
To address these risks, organizations must adopt responsible AI practices, such as those outlined in the World Economic Forum’s playbook for advancing responsible AI innovation.(World Economic Forum)
Accuracy vs Accountability in Future Predictions
Predictive tools promise future visibility but risk over‑confidence. Highly automated forecasting may present a veneer of scientific accuracy while failing to disclose uncertainty bounds or context. Accountability becomes crucial: firms must decide whether to trust black‑box predictions or maintain interpretative roles for analysts.
Balancing accuracy and accountability requires integrating human judgment into machine predictions.
Decentralized Market Research: Innovation or Information Chaos?
Blockchain‑Backed Data Collection
Decentralized Market Research platforms leveraging blockchain promise tamper‑proof data records and consumer‑controlled privacy. These technologies aim to resolve trust issues inherent to centralized databases, enabling participants to grant selective access to their data in exchange for value.
However, federated data sources can fragment insights if not harmonized, creating analytical complexity.
Centralized vs Decentralized Market Research Models
| Feature | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Data Control | Company | Consumer |
| Privacy | Medium | High |
| Integration | Easy | Challenging |
| Trust | Variable | Potentially High |
| Scalability | High | Variable |
Fragmented Sources vs Unified Insights
Decentralized approaches empower individual privacy but risk creating analytical silos. When data is scattered across platforms without standardized formats, deriving unified insights becomes cumbersome. Yet, for privacy‑first brands, decentralized frameworks can reinforce trust and spur new research paradigms.
Innovation demands new analytic tools capable of bridging decentralization with coherent strategy.
The Corporate Temptation to Over‑Automate
Efficiency Metrics vs Data Integrity
The corporate drive toward efficiency incentivizes over‑automation in Market Research. Automated dashboards produce metrics quickly, but speed sacrifices depth when companies ignore data integrity indicators. Organizational leaders risk accepting superficial results simply because they are delivered faster.
A MIT Technology Review analysis underscores how unchecked automation can degrade strategic insight when systems lack human oversight.(Deloitte)
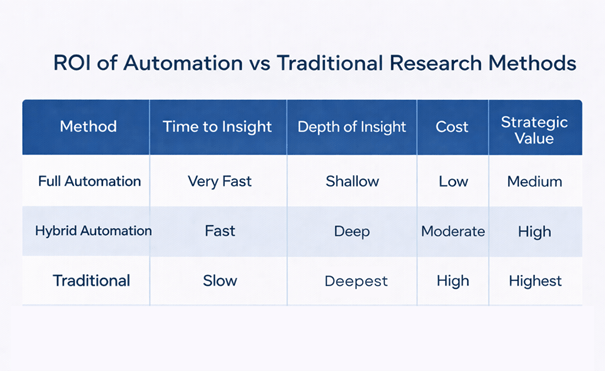
When Speed Undermines Strategy
Fast insights are seductive, yet businesses that prioritize speed over critical evaluation can misread trends and misallocate resources. True strategic advantage lies not in being first with a flawed answer but in being right with a validated one.
Market Research Talent in 2030: Obsolete or Irreplaceable?
Human Analysts in an AI‑Dominated Field
The idea that AI will replace all human analysts in Market Research is flawed. While machines excel at pattern recognition, they cannot conceptualize context, moral implications, or strategic nuance. Human analysts act as custodians of interpretation, transforming raw AI outputs into actionable strategic narratives.
The path to 2030 lies not in obsolescence but in human evolution alongside machines.
Training the Next Generation for Tech‑Augmented Research
Tomorrow’s market research professionals must be bilingual: fluent in analytical reasoning and computational tools. Training programs that combine analytical frameworks with AI tool mastery will produce talent capable of navigating complex datasets and ethical dilemmas.
Essential Human Skills in the Age of AI
- Strategic interpretation of AI outputs
- Ethical evaluation of data models
- Contextual reasoning across cultures and markets
- Cross‑disciplinary communication
- Continuous learning attitude

Market Research in 2030 Demands Human‑AI Synergy
By 2030, Market Research will be at a crossroads where automation can either elevate strategic insight or catalyze costly errors. Technology alone is insufficient. Machines generate volumes; humans validate meaning. Automation unlocks scale in data collection and pattern recognition, yet deep customer satisfaction understanding still requires human empathy and critical judgment. The most successful organizations will forge hybrid models where AI augments human reasoning without usurping it. Ethical oversight, transparency, and continuous learning will separate leaders from followers. In the relentless march toward automated intelligence, over‑reliance on machines without scrutiny invites automated mistakes. The future of market research does not lie in choosing humans or machines but in harnessing both with discipline and foresight.
References
Advancing Human-AI Collaboration – Deloitte
The AI Tools That Are Transforming Market Research – Harvard Business Review
The State of AI in 2023 – McKinsey
The Future of Customer Service – IBM
Advancing Responsible AI Innovation – World Economic Forum
Ai Market Research Revolution – H-in-Q



