The Double-Edged Sword of Open Source in MLOps
MLOps has become the critical layer for delivering real-world AI as merging machine learning, software engineering, and operations. At the heart of this transformation lies open source. From TensorFlow to Kubeflow, open ecosystems have democratized access, reduced cost, and accelerated progress. But this liberation isn’t without consequences. Every open line of code is a potential backdoor. Every unchecked contribution is a liability. As AI systems scale, the very openness that fuels speed and collaboration threatens to undermine the integrity, security, and governance required at the enterprise level. The question isn’t whether open source is good or bad for MLOps, it’s whether innovation can coexist with accountability. As organizations shift toward automated, scalable AI systems, they must ask: are they building on a foundation of shared strength or shared vulnerability?
Open Source as the Engine of Innovation in MLOps
Accelerated Development Through Collaborative Codebases
Open source propels MLOps with velocity rarely matched by proprietary tools. It allows cross-functional teams to iterate faster, build smarter, and adapt more easily. Developers across the globe contribute fixes, enhancements, and optimizations in real time. This collective intelligence compresses innovation cycles and democratizes access to powerful MLOps stacks.

Benefits of open source for MLOps acceleration:
- Rapid prototyping with reusable modules
- Access to battle-tested libraries and integrations
- Community-driven innovation and support
- Zero license costs for initial adoption
- Compatibility across hybrid environments
Automation at Scale : The Role of Open Source in Streamlining Pipelines
Open source tools underpin end-to-end MLOps automation. From continuous integration to model deployment, platforms like MLflow, Metaflow, and Argo drive process automation that scales with ease.
The Deployment Model of Cloud Computing and Open Source Synergy in MLOps
How Cloud-native Architectures Leverage Open Frameworks
Cloud infrastructure acts as a natural partner to open source MLOps. Most open source frameworks are designed cloud-first, enabling seamless integration with the deployment model of cloud computing be it IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS. This synergy offers unmatched scalability and adaptability.
Open Source Tool Compatibility by Cloud Deployment Model
| Cloud Model | Compatible MLOps Tools | Flexibility | Control Level |
| IaaS | Kubeflow, MLflow, DVC | High | High |
| PaaS | SageMaker (w/ open plugins) | Medium | Moderate |
| SaaS | DataRobot (limited OSS use) | Low | Low |
Multi-cloud Complexities: Flexibility vs Fragmentation
Open source promises portability, but the reality is fragmented. MLOps teams juggling AWS, Azure, and GCP often face configuration drift and tool incompatibility. Every deployment model of cloud computing introduces its own quirks, breaking the “build once, run anywhere” ideal.
The Data Pipeline Dilemma: Openness vs Integrity
Building Agile Data Pipelines with Open Tools
Data pipelines are the bloodstream of MLOps. Open tools like Apache Airflow and Luigi enable agile orchestration, while Kubeflow Pipelines offer ML-specific adaptability. Open source makes it easier to connect disparate data sources, but agility comes at a cost.
Popular open source data pipeline tools:
- Apache Airflow: Widely used for scheduling and orchestration
- Luigi: Task dependency management for batch jobs
- Kubeflow Pipelines: ML-focused pipeline management
- Dagster: Type-safe pipeline definitions
- Prefect: Hybrid orchestration with observability
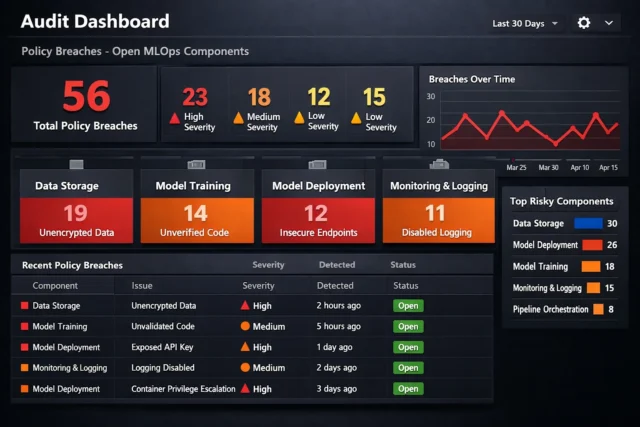
Where Data Ops Meets Risk: Open Source as Attack Surface
Every open integration point can be a target. Open-source tools often lack comprehensive security features by default. Inconsistent patching, outdated dependencies, and poorly governed community contributions widen the threat landscape across the data pipeline.
Data Breach Incidents Involving Open MLOps Tools (2021–2024)

Control Version in Open Source MLOps: Transparency or Chaos?
GitOps, Model Versioning, and Collaborative Tracking
MLOps thrives on reproducibility, and version control is the backbone. Tools like DVC and MLflow offer transparency into every model iteration and dataset change. GitOps extends this to infrastructure, allowing declarative deployments.
Version Control Tools for MLOps
| Tool | Focus Area | Strength |
| DVC | Data & model versioning | Git-compatible, scalable |
| MLflow | Model tracking | Metrics + lifecycle support |
| Git-LFS | Large file support | Model artifact storage |
When Version Control Becomes a Liability
Transparency is only valuable if it’s controlled. Open repositories with lax access permissions can expose sensitive model logic, private datasets, and internal workflows. Without strict governance, control version quickly becomes an operational nightmare.
AI Governance vs Open Source Freedom in MLOps
Aligning Open Tools with Enterprise AI Governance Frameworks
Mature organizations are embedding AI governance policies like bias mitigation, explainability, compliance, into their MLOps pipelines. Open source tools must be audited and adapted to meet these enterprise-grade standards.
Key governance priorities for open MLOps tools:
- Traceability and documentation of model decisions
- Compliance with data privacy regulations (GDPR, HIPAA)
- Bias detection in training datasets
- Explainable AI (XAI) integration
Open Source vs Compliance: The Unregulated Frontier
Open tools rarely bake in compliance. Many contributors aren’t thinking about legal exposure or regulatory scrutiny. Enterprises deploying models built on open code assume the full risk of violations.
DevOps, MLOps, and the Automation Arms Race
Merging DevOps with MLOps: Open Source as Common Ground
DevOps and MLOps converge on principles of automation, CI/CD, and version control. Open tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Argo unify these worlds, enabling seamless experimentation-to-deployment pipelines.
- CI/CD pipelines for code and model deployments
- Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) for scalable environments
- Unified logging and observability
When Automation Exceeds Control
Too much automation becomes a liability. Misconfigured CI/CD scripts have deployed untested models to production. Without rigorous testing gates, automation amplifies every flaw at speed.
The Enterprise Paradox: Trusting What You Don’t Control
Community Trust vs Enterprise Risk Management
Open source thrives on trust: that contributors act in good faith, that projects will be maintained, and that bugs will be patched. Enterprises, however, operate in a world of accountability. Security reviews, SLAs, and liability insurance don’t apply to GitHub.
Enterprise vs Community Open Source Project Comparison
| Criteria | Community Project | Enterprise Fork |
| Update Frequency | Irregular | Scheduled |
| SLA Availability | None | Yes |
| Security Reviews | Ad hoc | Mandatory |
| Governance Model | Decentralized | Controlled |
Should MLOps Teams Fork or Build Proprietary Overlays?
For critical infrastructure, some companies fork open tools or build proprietary wrappers to regain control. While this increases overhead, it enables internal security hardening, compliance integration, and long-term stability.
Choose Innovation, Secure Relentlessly
Open source is not a liability, it’s a weapon. In the hands of prepared, security-conscious enterprises, it enables unprecedented scale and speed in MLOps. But ignoring the risks of uncontrolled contributions, fragmented pipelines, and absent governance is a gamble with enormous downside. The challenge isn’t to abandon open source, it’s to master it. Organizations that succeed will layer governance on top of freedom, inject control into automation, and turn community chaos into enterprise-grade clarity. The alternative? Watch innovation unravel under the weight of its own negligence. Open source won the race for relevance in MLOps. Now it must earn the right to stay.
References
How Open Source Is Accelerating MLOps Innovation — Harvard Business Review
AI Governance and MLOps: The New Compliance Frontier — McKinsey
The Importance of Secure Open Source for MLOps Pipelines — MIT Technology Review
Enterprise Cloud and Open Source: A New Operating Model — IBM
Why MLOps Needs DevSecOps — Deloitte
mlops-data-lineage-transparency-vs-overhead — H-in-Q



