Industry 4.0 and the IoT Dilemma: Progress at What Cost?
The fourth industrial revolution, Industry 4.0, is no longer a speculative frontier it is operational, ubiquitous, and surging through factories, supply chains, and infrastructure worldwide. Fueled by the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR), it promises unimaginable efficiency. Machines talk to machines. Decisions are made in milliseconds. Virtual overlays guide workers through complex tasks. But this hyperconnected, intelligent ecosystem comes with a sinister undercurrent: cybersecurity is failing to keep pace. Every new sensor, every augmented reality zone, and every machine to machine handshake opens a new attack surface.
So the debate is unavoidable: is Industry 4.0 a seamless integration of revolutionary technology, or is it a sprawling cybersecurity nightmare waiting to implode? This article does not sit on the fence. It argues that while the risks are real and growing, the solution lies in doubling down on AI and secure design, not in slowing progress.
The Promise of Industry 4.0: Integration, Automation, and Intelligence
How IoT Supercharges Industry 4.0 Efficiency
IoT is not just enabling Industry 4.0 it is driving it. The convergence of sensors, edge computing, and cloud analytics forms the nervous system of the smart factory. Machines do not just execute tasks anymore; they learn, adapt, and optimize in real time. Downtime is minimized through predictive maintenance, and resource use is optimized down to the second.
According to a McKinsey report on IoT’s impact, IoT-driven productivity improvements could add up to $3.7 trillion to the global economy annually. The Industrial IoT (IIoT) makes real-time visibility a default, not a luxury.
- Real-time asset tracking
- Predictive maintenance
- Automated quality control
- Remote operations via augmented interfaces
From Augmented Reality to Predictive Maintenance
AR adds another layer to this evolution. In the augmented reality zone, technicians receive overlaid instructions, guided diagnostics, and live expert support all hands free. Predictive maintenance becomes proactive with AR visualizations warning of equipment anomalies before they escalate.

Cybersecurity in Industry 4.0: The Exploding Threat Surface
Why IoT Makes Industry 4.0 Vulnerable by Design
Every connected device every sensor, actuator, or AR interface represents a possible vulnerability. Industry 4.0 is built on a sprawling web of connected systems that often lack uniform security protocols.
The problem? Legacy systems were not built for connectivity, let alone cybersecurity. Layering IoT on top of them is like installing smart locks on a house with broken windows.
As Deloitte points out in their analysis of cyber risk in manufacturing, an interconnected ecosystem increases potential entry points for attackers. This means a single weak link can compromise entire networks.
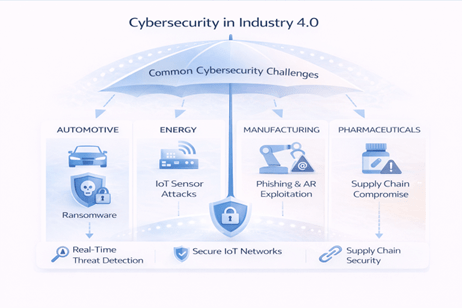
Case Studies in Catastrophic Breaches
- A 2021 ransomware attack halted operations at a global meat processor through a compromised industrial controller.
- A major European carmaker suffered millions in downtime after a vulnerable IoT sensor was exploited.
- In 2023, attackers hijacked an AR training system in an oil refinery injecting false data into maintenance protocols.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Industry 4.0
Augmented Reality in Industry 4.0: Innovation or Infiltration Point?
Augmented Reality Elements Driving Industrial Transformation
Augmented reality is not just a cool interface it is a core driver of Industry 4.0. AR powered digital twins, guided maintenance, and immersive training reduce error rates and accelerate production. AR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap are becoming industrial standards.
The Augmented Reality Meta: A New Attack Vector?
But every AR headset streams data, syncs to the cloud, and interfaces with machines. That means every AR device becomes a potential gateway for intrusion. Worse, AR vulnerabilities are often under researched and under regulated.
AR Use Cases vs Cyber Vulnerability Risk
| Use Case | AR Value Add | Cyber Risk Level |
| Remote maintenance | Reduced downtime | High |
| Training simulations | Faster onboarding | Medium |
| Real-time quality checks | Error reduction | High |
| Inventory management | Accuracy and speed | Low |
Regulatory Paralysis: Industry 4.0 Moves Faster Than the Law
Why Current Cyber Laws Can’t Keep Up with IoT Integration
Industry 4.0 evolves on quarterly innovation cycles; legislation takes years. There is a regulatory chasm between what governments can mandate and what corporations deploy. Most cyber laws were drafted before IoT was widespread, and almost none account for AR vulnerabilities.
The Price of Innovation Without Accountability
This vacuum allows vendors to ship insecure products and lets companies delay necessary upgrades. Without legal pressure, cost-cutting trumps cybersecurity every time.
Key Legal Gaps in Industry 4.0 Regulation
- No mandatory IoT firmware update requirements
- No AR device encryption standards
- Lack of cross-border data handling regulations
- No clear liability frameworks for IIoT breaches
Security-First Design: Can Industry 4.0 Be Rebuilt from Within?
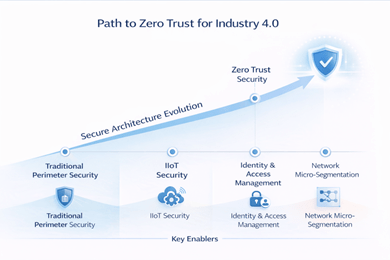
Zero Trust Architectures in Industrial IoT
Trust no one, verify everything is the new mantra. Zero Trust architectures, when implemented, can reduce breach potential dramatically. This model assumes every device and user could be compromised and treats them accordingly. You can explore more about this at the Harvard Business Review’s guide to Zero Trust.
Security by Design in the Augmented Reality Zone
Integrating secure protocols into AR platforms from the ground up is essential. That means encrypted visual streams, hardened firmware, and limited cloud exposure.
Secure Architecture Adoption in Industry 4.0
Public vs Private: Who Owns Cybersecurity in Industry 4.0?
The Corporate Responsibility Debate
Should private enterprises shoulder the full burden of securing Industry 4.0 systems? Most argue yes after all it is their data, reputation, and operations at stake. But many corporations still invest less than 3 percent of their IT budget into cybersecurity.
Can Governments Enforce Digital Sovereignty in IoT Ecosystems?
Digital sovereignty is a rising concern. Countries like Germany and Japan are creating frameworks to force IoT vendors to comply with national cybersecurity standards a trend that is gaining traction. For deeper insights see the World Economic Forum’s report on digital governance.
Cybersecurity Investment Government vs Corporate
| Region | Corporate Spend | Government Investment |
| US | $18B | $6B |
| EU | $13B | $5B |
| China | $15B | $10B |
AR, IoT, and AI: The Unstoppable Trifecta of Industry 4.0
Why the Augmented Reality Zone is Inevitable
AR is not a novelty. It is a strategic advantage. Whether in automotive, aerospace, or logistics, the augmented reality zone provides the precision and speed modern industry demands. Blocking AR for fear of risk is as outdated as banning email for fear of spam.
AI as the Ultimate Safeguard for Industry 4.0
The only force capable of defending Industry 4.0’s complexity is AI itself. Machine learning can monitor anomalies, detect intrusions, and adapt in real time beyond human capabilities. According to IBM’s analysis of AI in cybersecurity, AI-enhanced systems reduce breach response times significantly.
Strategic Advantages of the AI AR IoT Fusion
- Real-time intrusion detection
- Predictive system hardening
- Automated threat remediation
- Continuous learning from global attack patterns

Cybersecurity May Be the Price of Progress But It Is a Bill Worth Paying
Let us not kid ourselves: Industry 4.0 is vulnerable. The more integrated the system the higher the stakes. But halting innovation is not the answer it is surrender.
AI, zero trust, and security by design are not just technologies they are mandates. Regulation must catch up. Enterprises must lead not wait. And the fusion of AR, IoT, and AI must be treated not as a luxury but a necessity for resilience. The augmented reality meta and augmented reality zone are not threats in themselves negligence is. With the right architecture and urgency Industry 4.0 does not have to choose between progress and security. It can and must have both
References
- The Internet of Things: Mapping the Value Beyond the Hype – McKinsey
- Cyber Risk in Advanced Manufacturing – Deloitte
- Zero Trust Security: What It Is and How to Get Started – Harvard Business Review
- The Global Risks Report 2023 – World Economic Forum
- How AI Is Transforming Cybersecurity – IBM
- Industry 4.0’s Digital Twins: Smart Optimization or Surveillance in Disguise? – H-in-Q



