The Augmented Frontier: AR and Industry 4.0’s Tipping Point
Industry 4.0 has already begun to reshape manufacturing through connectivity, data, automation, and analytics. (McKinsey & Company) Into that transformation steps Augmented Reality (AR), a technology promising to overlay digital insights onto physical reality. Some hail AR as the “missing link” capable of elevating Industry 4.0 into seamless human‑machine symbiosis. Others dismiss it as a futuristic distraction: costly, immature, and misaligned with real industrial pain points. This article argues AR could be the strategic catalyst Industry 4.0 needs to transcend early‑stage digitization and deliver scalable value.
The Evolution of Industry 4.0: A Data‑Driven Revolution
From Automation to Intelligence in Industry 4.0
The journey from steam engines to cyber‑physical systems charts humanity’s industrial progress. The first revolution mechanized labor, the second brought electricity, the third triggered basic automation. Now Industry 4.0 combines sensors, cloud computing, analytics, AI, robotics and human–machine interaction, including AR. (McKinsey & Company) Its foundations: connectivity and data; analytics and intelligence; human–machine interaction; advanced manufacturing techniques. (McKinsey & Company) This shift defines a new era: real‑time feedback loops, agility, customization, and digital twins driving operational excellence.
Industrial Revolutions Compared
| Revolution | Core Driver | Key Outcome | Relevance to Industry 4.0 |
| 1st | Steam / mechanization | Mass production | Historical baseline |
| 2nd | Electricity / assembly lines | Speed & scale | Legacy factory structures |
| 3rd | Automation / electronics | Reliability, repeatability | Precursor to digitization |
| 4th (Industry 4.0) | Connectivity, data, AI, robotics, human–machine interaction | Agility, customization, intelligence | Enables AR + digital‑physical convergence |
![]()
Adoption of Industry 4.0 is uneven. Many companies remain stuck in “pilot purgatory”: trials without scale, yielding limited impact. (McKinsey & Company) The core challenge: deploying enabling technologies systematically across people, processes, and infrastructure.
Augmented Reality Elements That Redefine Production Lines in Industry 4.0
Visualizing Efficiency in Industry 4.0 with augmented reality elements
AR introduces a set of augmented reality elements uniquely suited to the demands of Industry 4.0:
- Real‑time digital overlays on machinery, highlighting performance metrics or fault warnings.
- Spatial analytics dashboards, letting workers visualize heat maps, workflow patterns, or resource flows directly on the shop floor.
- Digital twins with live annotations, enabling virtual replicas of machines with interactive controls.
- Human-in-the-loop guidance step‑by‑step work instructions, error‑proofing, and quality checks.
- Collaborative remote assistance, connecting on‑site workers with experts anywhere in the world.
These augmented reality elements transform raw data into actionable insight, merging digital intelligence with physical action. Factories can forego cumbersome control rooms, workers see what matters where it matters.
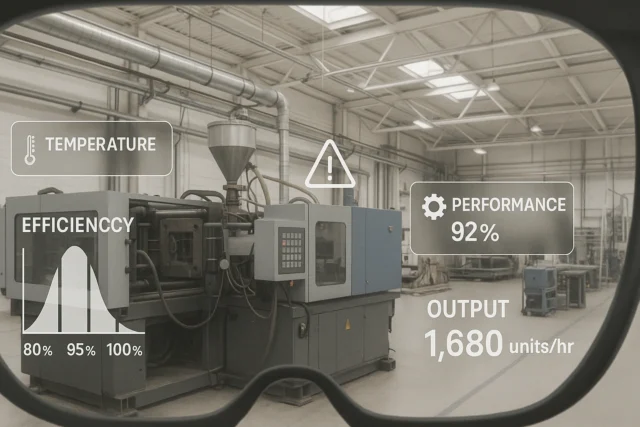
This is not “meta.” By surfacing meaningful context where decisions are made, AR shifts Industry 4.0 from abstract dashboards to tangible floor‑level intelligence.
The Business Case for Augmented Reality in Industry 4.0
Productivity or Hype in Industry 4.0 augmented reality
Executives evaluating Industry 4.0 increasingly consider AR not as a gadget, but as a strategic lever. A 2020 analysis of companies leading the digital transformation revealed that human–machine interaction (explicitly including AR) was among the four foundational technology clusters driving performance. (McKinsey & Company)
Companies piloting AR early report measurable gains: faster machine maintenance, reduced downtime, and accelerated training cycles.
AR ROI Snapshot : Selected Industrial Use Cases
| Company / Site | Use Case | Reported Benefit |
| Aerospace manufacturer | AR-guided assembly instructions | 25% reduction in assembly time |
| Machinery plant | AR maintenance overlays | 30% fewer unplanned downtimes |
| Electronics factory | AR-based quality checks | 40% decrease in defect rate |

The promise: AR delivers value across ROI levels; productivity, quality, speed, agility. Combined with AI and data analytics, AR can accelerate decision‑making and shrink the gap between insight and action. In the age of Industry 4.0, that speed may be the difference between leading and lagging.
The Skeptic’s View: Is Augmented Reality a Meta‑Fantasy in Industry 4.0
Cost, Complexity and Culture Clash in Industry 4.0 augmented reality meta
Skeptics question whether AR delivers more than marketing hype. Critics highlight five core concerns: high integration cost; immature or unreliable software; lack of standardization; workforce resistance; and cognitive overload. Recent academic reviews note that while AR shows potential, actual industrial adoption remains limited. (ScienceDirect)
Pros vs Cons of AR Adoption in Industry 4.0
| Pros | Cons / Risks |
| Real‑time contextual insights | High upfront cost (hardware + training) |
| Shorter training cycles | Immature or buggy AR software |
| Improved safety and quality | Lack of interoperability between platforms |
| Better decision-making speed | Worker resistance, ergonomics issues |
| Competitive differentiation | Unclear long‑term ROI in some use cases |

Moreover, some studies highlight that a majority of AR applications in industry remain at pilot stage with limited scaling. (ScienceDirect) In organizations lacking digital infrastructure or data maturity, AR may become a costly distraction rather than a value driver.
This is the “augmented reality meta‑fantasy”: a shiny promise that glosses over infrastructure debt, organizational change, and human factors.
The Augmented Reality Zone: Immersive Training Solutions in Industry 4.0
Workforce Development in Industry 4.0 augmented reality zone
Training and skills gaps remain one of the biggest bottlenecks for Industry 4.0 scaling. AR offers a powerful solution: immersive, contextual, scalable learning experiences. According to a project by MIT, AR‑based manufacturing‑education apps allow learners to visualize 3D disassembly or assembly tasks in their real environment without physical tools. (meche.mit.edu)
AR Training Performance : Sample Metrics
| Metric | Traditional Training | AR-based Training |
| Time to competency | 12 weeks | 7 weeks (‑42%) |
| Error rate during training | 15% | 5% (‑67%) |
| Equipment downtime due to training errors | High | Low |

AR training creates an “augmented reality zone” where employees can experiment, learn, and interact without risk. For Industry 4.0 adopters, this isn’t optional. With faster onboarding, fewer mistakes, and better retention, AR-enabled training addresses one of the hardest challenges in digitized manufacturing: human readiness.
Integration Challenges : Interoperability or Isolation in Industry 4.0 AR Ecosystems
Platform Wars and Closed Systems in Industry 4.0 augmented reality integration
AR’s potential collides with a fragmented ecosystem. Multiple vendors; hardware and software; offer mutually incompatible platforms. Without common standards, companies risk vendor lock-in. Developing a scalable Industry 4.0 strategy with AR requires foresight and architectural discipline.
Key industrial AR platforms currently in use include:
- AR smart glasses (various vendors)
- Tablet or smartphone‑based AR applications
- Edge‑computing + digital‑twin AR systems
- Cloud‑based AR collaboration tools
These platforms often require custom integration with existing IIoT, ERP, or PLM systems, increasing complexity.
Augmented Reality Devices in Industry 4.0 Integration
Without open APIs or industrial AR standards, each deployment becomes a bespoke project, limiting scalability. The risk: AR becomes a siloed “zone” rather than a connected component of the Industry 4.0 ecosystem.
Real‑Time Decision Making: Why AR Matters for Industry 4.0’s Next Phase
Rapid Response and Strategy in Industry 4.0 augmented reality environments
Industry 4.0 is about digitizing assets and accelerating decisions too: maintenance, quality control, supply‑chain disruptions. AR enhances real‑time situational awareness: workers see live data overlays, maintenance crews get guided workflows, managers view heatmaps and KPIs directly on site. These real‑time decision loops shorten the time between insight and action.
In traditional factories, decision cycles can span hours or days; data gathered, analyzed, and then acted on. With AR-enhanced workflows, decision cycles shrink to minutes: sensor triggers, alert overlays, immediate on‑floor intervention. In fast‑moving environments, that speed reduces downtime and increases responsiveness.

This capability transforms Industry 4.0 from a loosely digital overlay into a living, reactive system: where data flows into the hands of people in real time. The result: greater agility, fewer disruptions, and a smarter, leaner operation.
AR As Imperative Catalyst in Industry 4.0
AR is a strategic accelerator for Industry 4.0. It binds together data, machines, and people in ways that desktop dashboards never could: context‑rich, real‑time, actionable. Where skeptics see cost and complexity, early adopters see scalable value: faster training, reduced downtime, better decision‑making, and competitive advantage. AR’s limitations such as fragmented platforms, integration overhead, immature applications are real, but they do not outweigh the potential benefits for those ready to architect wisely and commit to scale. Companies that dismiss AR risk losing the productivity gains and human capital advantages that define tomorrow’s smart factories. Industry 4.0 without AR will be incomplete, uninspired digitization at best and a squandered revolution at worst.
AR must be embraced now not as a gimmick but as a core enabler driving Industry 4.0 toward its full promise.
References
- What are Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and 4IR? – McKinsey
- Capturing Value at Scale in Discrete Manufacturing – McKinsey
- Reimagining Manufacturing Operations Post-COVID-19 – McKinsey
- Augmented Reality for Manufacturing Education – MIT Mechanical Engineering
- Systematic Review of Augmented Reality in Industry 4.0 – ScienceDirect
- age of cobots working together or working ourselves out of a job – H-in-Q



